workshop-ai-100
Process and classify images with the Azure Cognitive Vision Services
Microsoft Cognitive Services offers pre-built functionality to enable computer vision functionality in your applications. Learn how to use the Cognitive Vision Services to detect faces, tag and classify images, and identify objects.
In this tutorial you will:
- Create, train and test a custom image classification model using the Custom Vision Service to accurately identify paintings from famous artists.
Create a Custom Vision Service project
The first step in building an image-classification model with the Custom Vision Service is to create a project. In this unit, you will use the Custom Vision Service portal to create a Custom Vision Service project.
-
Open the [Custom Vision Service portal] (https://www.customvision.ai/) in your browser. Then select Sign In.
-
If you are asked to sign in, do so using the credentials for your Microsoft account. If you are asked to let this app access your info, click Yes, and if prompted, agree to the terms of service.
-
Click New Project to create a new project.
-
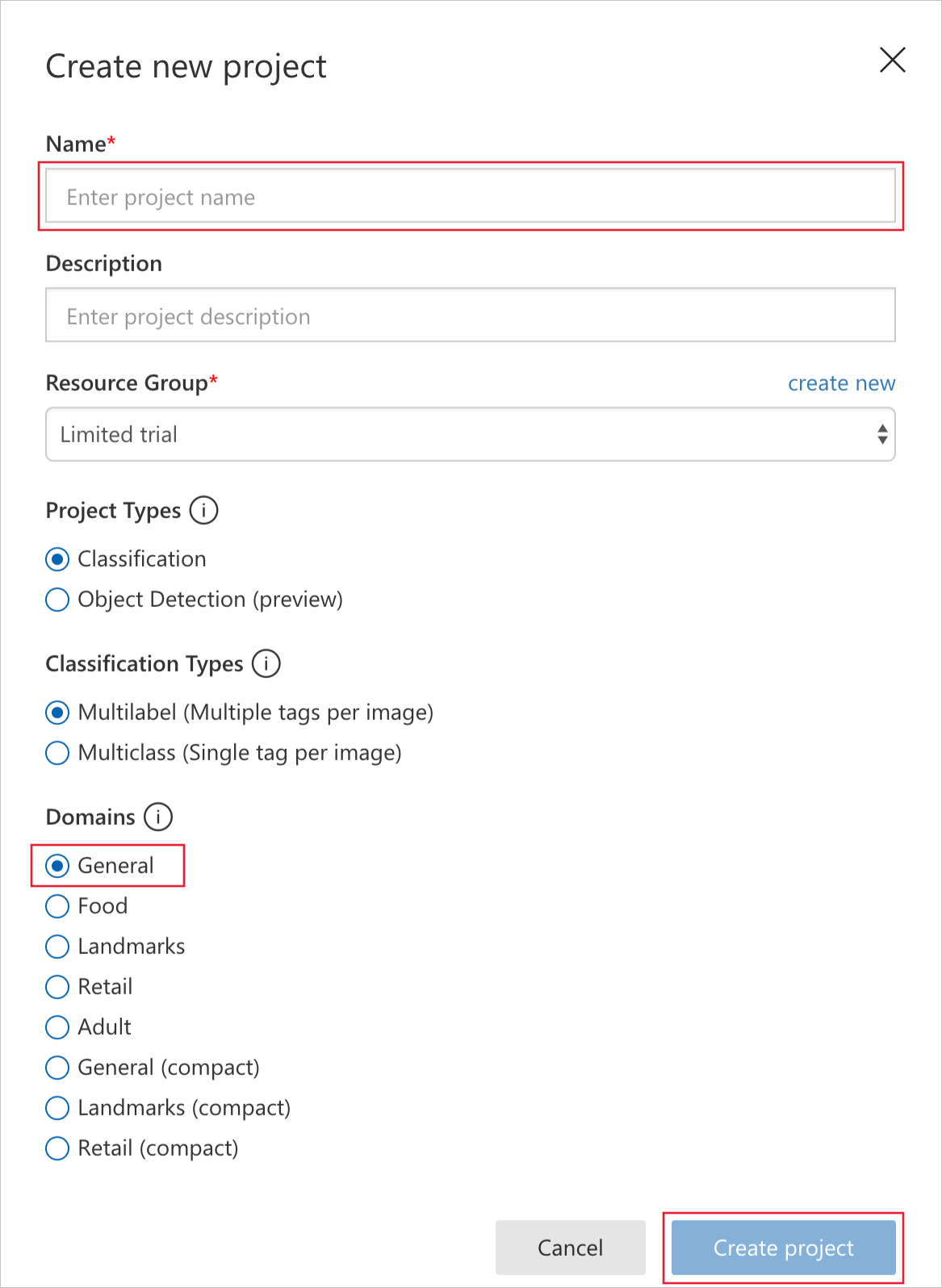
In the Create new project dialog, name the project Artworks.
-
Select the Resource Group you want to use for this project. If you do not already have a resource group, select create new to create a new resource group.
-
After you select the resource group, the following sections display:
-
Project Types: Select Classification.
-
Classification Types: Select Multilabel
-
Domains: Select General.
A domain optimizes a model for specific types of images. For example, if your goal is to classify food images by the types of food they contain or the ethnicity of the dishes, then it might be helpful to select the Food domain. For scenarios that don’t match any of the offered domains, or if you are unsure of which domain to choose, select the General domain.
- Select Create project to create our project.
The next step is to upload images to the project and assign tags to those images to classify them.
Upload tagged images
In this unit, you’ll add images of famous paintings by Picasso, Pollock, and Rembrandt to the Artworks project. You’ll tag the images so the Custom Vision Service can learn to differentiate one artist from another.
- In the Artworks project that we created, select the plus sign (+) to the right of Tags in the side panel.
-
A dialog called Create a new tag is displayed. Type painting into the tag name field and select Save. This operation creates the tag painting in the tag list. Let’s add some more.
-
Repeat steps 1 and 2 to add tags with the values Picasso, Pollock, and Rembrandt. The tag list will look like the following when you are finished.
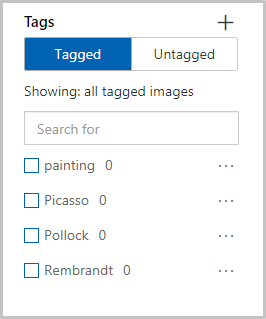
As you can see, the number of images in our project that are tagged with each of these tags is zero. Let’s add some images to our project and assign tags.
-
Download cvs-resources.zip which contains image resources for this module and unzip it to your local machine.
-
Back in the portal, select Add images to add images to the project.
-
In the cvs-resources folder that you downloaded locally in step 4, navigate to the “Artists\Picasso” folder.
-
Select all of the files in “Artists\Picasso”, and then select Open.
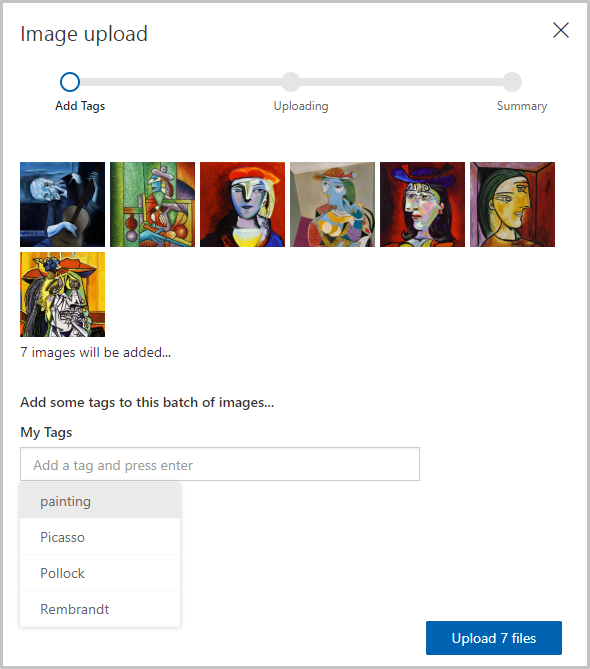
- The Image upload dialog appears and displays thumbnails of all the images we are uploading. Select the My Tags field, which opens a dropdown of the tags you can assign these images.
-
Select the tags painting and Picasso and then select Upload 7 files to finish the upload.
-
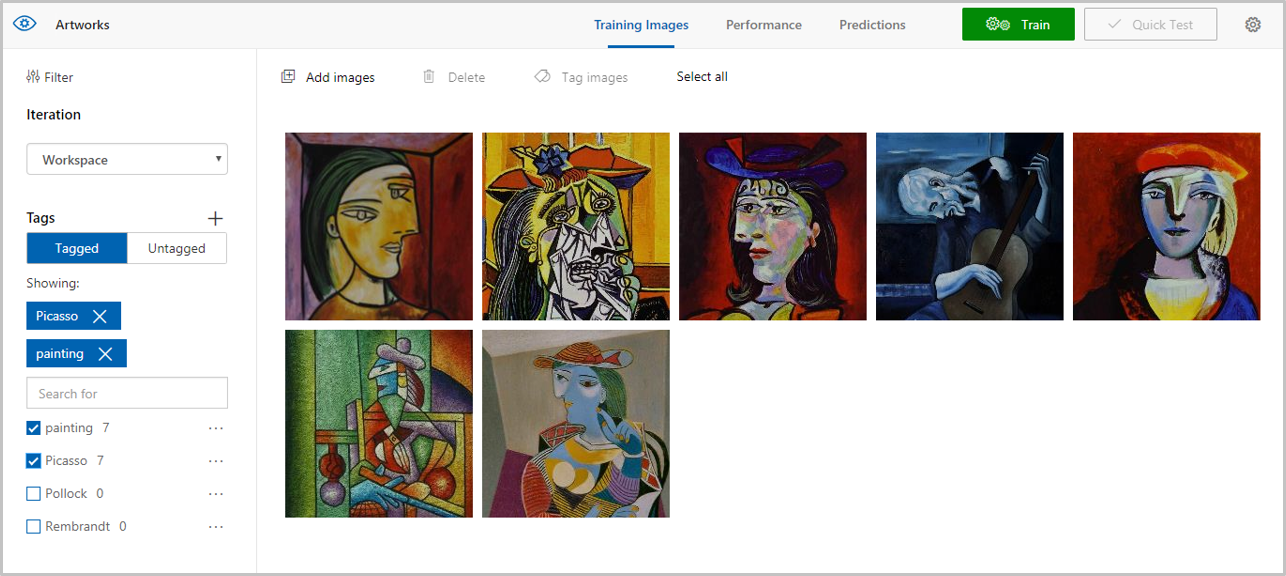
Confirm that the images you uploaded are now in the Artworks project, and that the tag list has been updated to show that we’ve tagged seven images with Picasso and painting.
-
With seven Picasso images, the Custom Vision Service can do a decent job of identifying paintings by Picasso. But if you trained the model right now, it would only understand what a Picasso looks like, and it wouldn’t be able to identify paintings by other artists. The next step is to upload some paintings by another artist.
-
Select Add images and select all of the images in the “Artists\Rembrandt” folder in the module resources. Tag them with the labels “painting” and “Rembrandt” (not “Picasso”), and select Upload 6 files to upload them to the project.
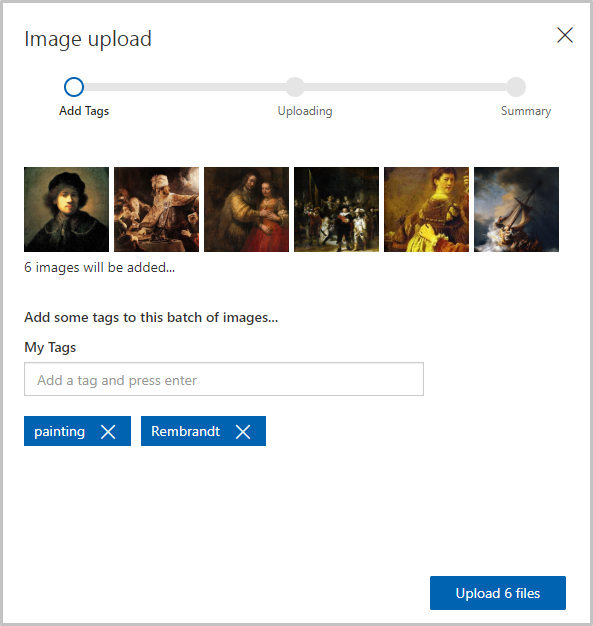
- Confirm that the Rembrandt images appear alongside the Picasso images in the project, and that “Rembrandt” appears in the list of tags.
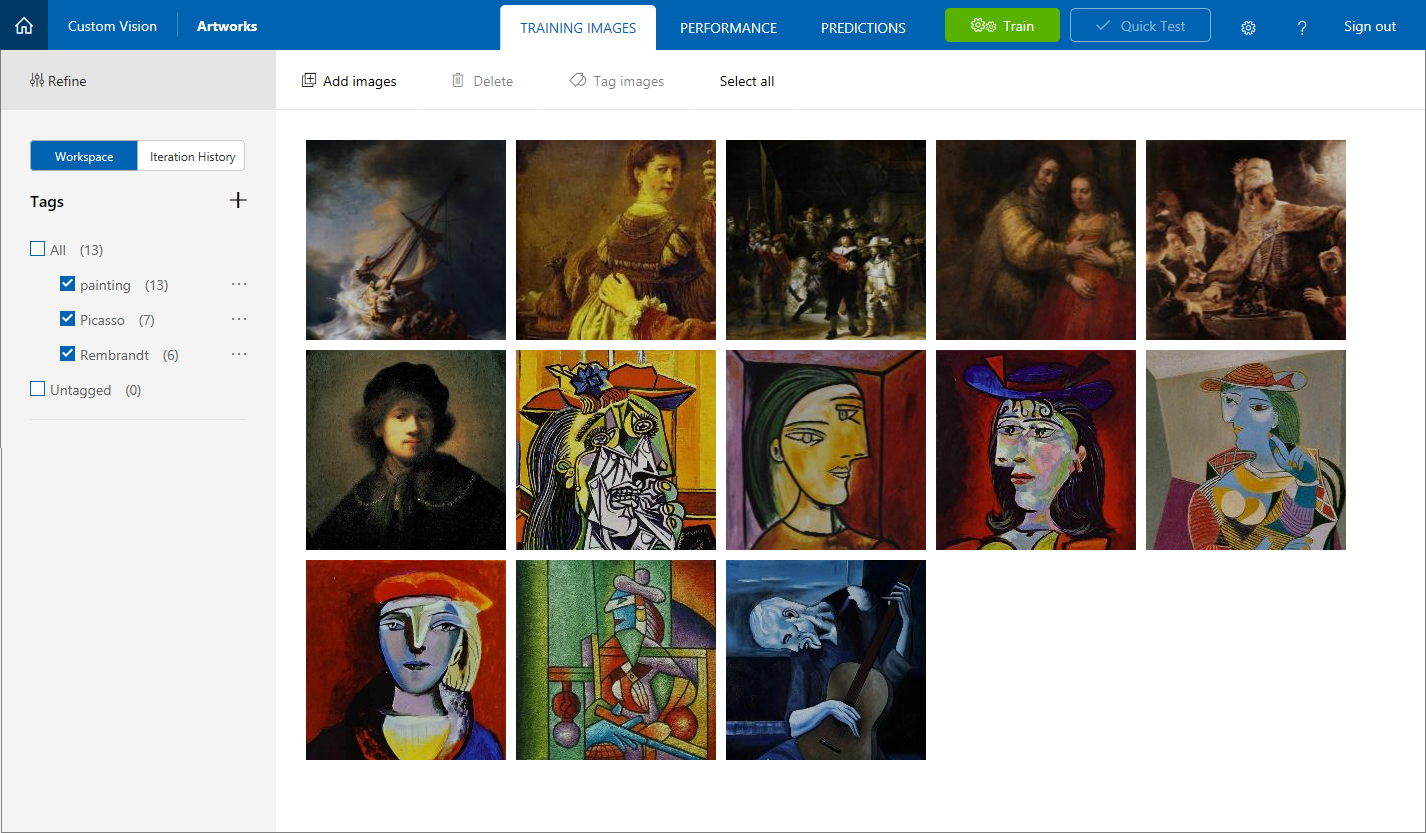
- Now add paintings by the enigmatic artist Jackson Pollock to enable the Custom Vision Service to recognize Pollock paintings, too. Select all of the images in the “Artists\Pollock” folder in the module resources, tag them with the terms “painting” and “Pollock”, and upload them to the project.
With the tagged images uploaded, the next step is to train the model with these images so it can distinguish between paintings by Picasso, Rembrandt, and Pollock, as well as determine whether a painting is a work by one of these famous artists.
Train the model
In this unit, you’ll train the model using the images uploaded and tagged in the previous exercise. After you train a model, you can refine it by uploading additional tagged images and retraining it.
- Click the Train button at the top of the page to train the model. Each time you train the model, a new iteration is created. The Custom Vision Service maintains several iterations, allowing you to compare your progress over time.

- Wait for the training process to finish. (It should take only a few seconds.) Then review the training statistics presented to you for iteration 1.
The results show two measures of a model’s accuracy, Precision and Recall. Suppose the model was presented with three Picasso images and three from Van Gogh. Let’s say it correctly identified two of the Picasso samples as “Picasso” images, but incorrectly identified two of the Van Gogh samples as Picasso. In this case, the Precision would be 50%, since it identified two out of four images correctly. The Recall score would be 67% since it correctly identified two of the three Picasso images correctly.
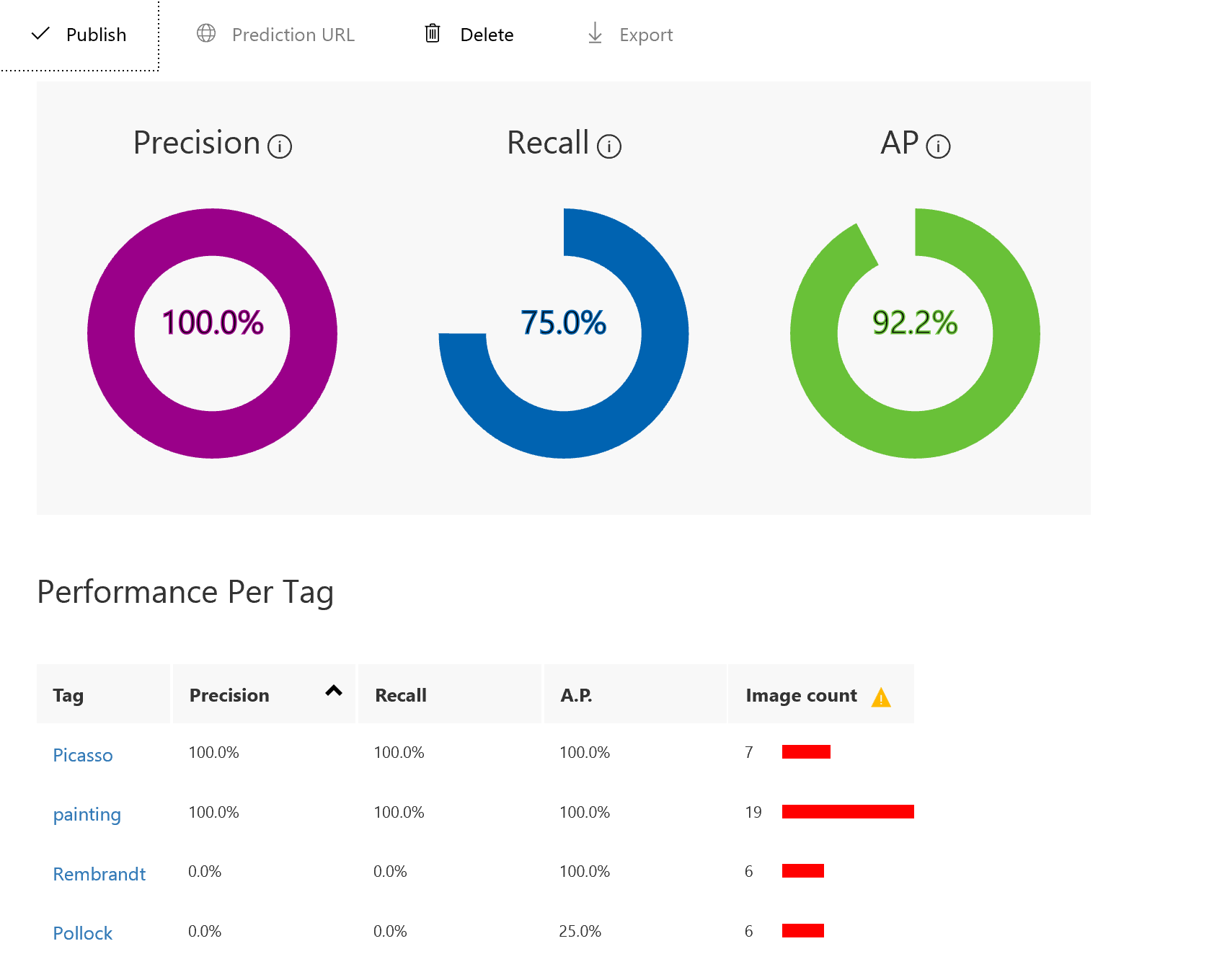
In the next exercise, we’ll test the model using the portal’s Quick Test feature, which allows you to submit images to the model and see how it classifies them using the knowledge gained from the training images.
In addition to training the model using the Custom Vision portal UI, you can also train it by calling the TrainProject method in the Custom Vision Training API.
Test the model
Now that we’ve trained our model, it’s time to test it. We’ll give the model new images and see how well it classifies it.
- Click Quick Test at the top of the page.

- Click Browse local files, and then browse to the “Quick Tests” folder in the module resources folder you download previously. Select PicassoTest_01.jpg, and click Open.
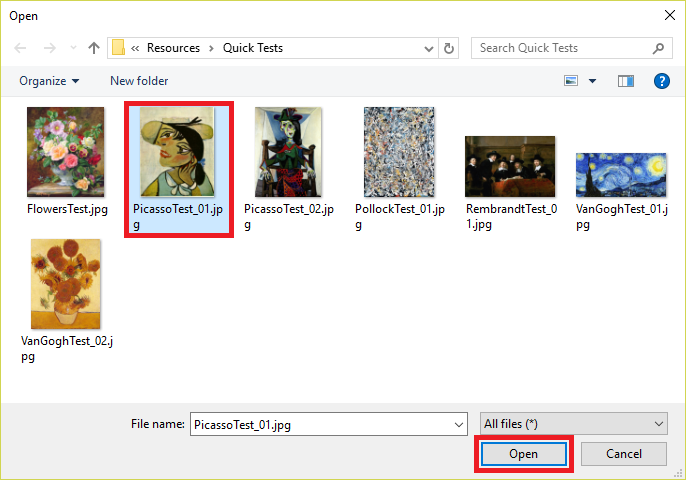
- Examine the results of the test in the “Quick Test” dialog. What is the probability that the painting is a Picasso? What is the probability that it’s a Rembrandt or Pollock?
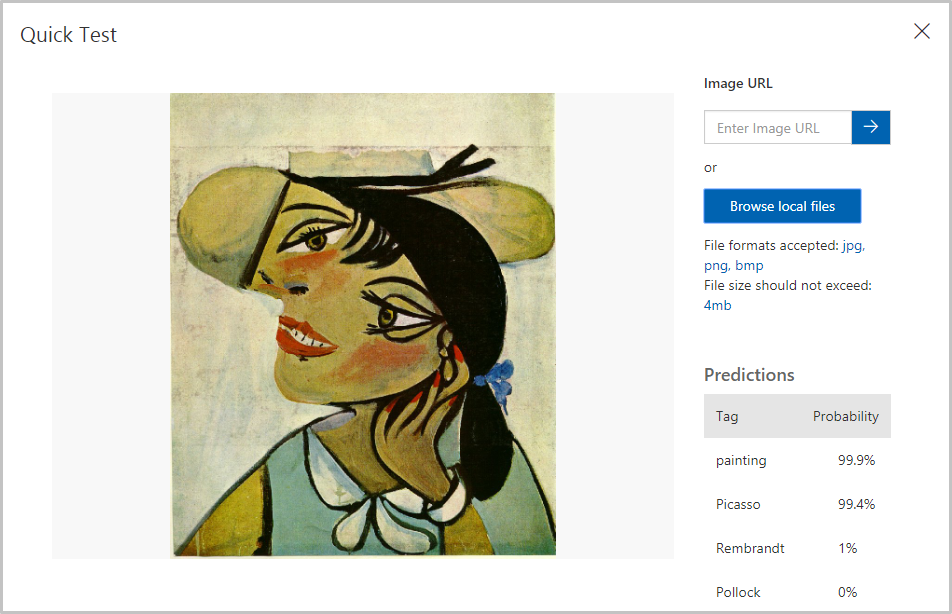
- Close the “Quick Test” dialog. Then click Predictions at the top of the page.

- Click the test image that you uploaded to show a detail of it. Then tag the image as a “Picasso” by selecting Picasso from the drop-down list and clicking Save and close. By tagging test images this way, you can refine the model without uploading additional training images.

- Run another quick test, this time using the file named FlowersTest.jpg in the “Quick Test” folder. Confirm that this image is assigned a low probability of being a Picasso, a Rembrandt, or a Pollock.
The model is trained and ready to go and appears to be skilled at identifying paintings by certain artists. You can call the prediction endpoint over HTTP and see what happens.